
In recent years, line array speaker systems have been widely used in large-scale sound reinforcement venues with their unique advantages. The line array speaker system is produced in response to market demand and is also a product of high-tech, so it has attracted people's attention.
The production of line array system speaker
In the 1960s and 1970s, rock music represented by the "Beatles" emerged in Europe and the United States. There were hundreds of thousands of spectators who went to the square to watch rock concerts, and sound reinforcement was a big problem. For example, 600,000 people participated in a rock concert held in New Jersey on September 3, 1977. The sound reinforcement system uses a "sound tower" composed of multiple speakers stacked together, which is very troublesome to install and debug. After careful design and debugging, a lot of energy was spent, and the sound reinforcement effect is always unsatisfactory. This phenomenon provides market information. Large-scale touring performances require sound reinforcement systems with high power and easy installation and debugging.
Some large companies are focusing on market demand and are committed to developing high-power, far-projection sound reinforcement systems. From the perspective of acoustics, there are two ways to obtain the effect of high power and far projection.
• One is the horn, which makes the sound energy radiate out in one direction through the horn to control the directivity, improve the radiation efficiency, and achieve the effect of far projection. For example, in the 1950s, we used large horns for the Kinmen and Matsu Broadcasting systems. A horn is more than ten meters long and has a transmission distance of several kilometers.
• The other is the speaker array proposed in the 1930s, which uses the principle of interference to control directivity. In fact, there was already a popular column type speaker-sound column. The sound column has a relatively narrow vertical directivity, but the power is not large enough, the projection is not far, and there are still some problems to be overcome, such as the dynamics and bandwidth of the sound. Some large companies have their own priorities according to their own circumstances.
The horn research has successfully developed constant directivity horn speakers, horn speakers with multiple drive units, etc. The French company L-Acoustics first introduced the V-DOSC system in 1993. It is an array composed of a row of unit speakers. The working principle is similar to that of a sound column. Its vertical directivity is controllable, determined by the number of unit boxes, and the horizontal radiation angle is 120°. The frequency response of each unit box is 50Hz~18kHz±3dB, the power is 1500W, and the sensitivity is 134dB. The high-frequency unit radiates outward through the waveguide. This is the first line array product launched, and it has attracted people's attention from the beginning.
The demand of the market, the development and application of high-tech, make the line array loudspeaker system become the iconic product of each company showing its strength. Now the line array is a combination of horn technology and array technology, making the radiation performance more perfect.
Features of concert line array speaker system
1. Regular arrangement of unit boxes
The line array speaker system is composed of a row of unit boxes, which are arranged according to a certain rule, and can be arranged in a straight line and a "J" shape according to the needs of the sound field. The number of unit boxes is determined by the requirements of the sound field, but must meet the basic requirements of forming a line array, that is, the length of the line array should be at least more than half of the wavelength of the radiated sound wave. The radiation characteristics of each unit box have strict requirements. For example, the radiated sound power, frequency characteristics, horizontal directivity, distortion and linear phase must meet the requirements of the line array.
2. High power and long projection distance
For example, the low-frequency unit in the unit box of Sanway Vera36 outdoor line array speaker has a power of 1000W and a sensitivity of 98dB; the intermediate frequency unit has a power of800W and a sensitivity of 110dB; the high-frequency unit has a power of 150W and a sensitivity of 112dB. After the unit boxes are formed into an array, due to the interaction between the unit boxes, the radiation impedance of the loudspeaker is improved and the radiation efficiency is improved. Therefore, it is easy to use a line array speaker system as a sound source to obtain a sound pressure level of 100dB or more beyond 100m.
3. The covered sound field is relatively uniform, the interference area is small, and the playback resolution is high
The vertical directivity of the line array is very sharp, generally around 10°, and the narrowest one can reach 3°. The radiated sound beam is narrow, the direct sound reaching the corresponding audience area is relatively strong, the radiated distance is relatively far, and the change in sound pressure level in a large area is relatively small. Due to the sidelobe control of the line array, the overlapping area of the radiated sound field is relatively small and the interference surface is small. The area dominated by direct sound has good hearing, clear sound and high resolution.
How does the pa line array speaker work?
How power line arrays work can be a fairly in-depth discussion. Here, we will not explain the details of the whole theory too detailed. The following will use simple language and mathematical calculations to let everyone first understand how the sound of a typical speaker spreads as the distance increases.
1. inverse square law
The content of the inverse square law in acoustics is that the magnitude of sound intensity and the distance between the listening position and the sound source are inversely proportional to the square. The result is that every time the distance between the listener and the point source doubles, the sound pressure is attenuated by 6dB. This is the performance of the speakers we usually use, although there are many subtle differences between actual and theoretical.
2. Point source
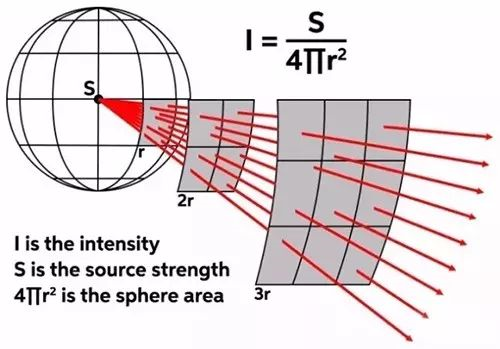
The premise of the inverse square law is that the speaker can radiate Omni directionally. For physical speakers, this situation is rare, unless the speakers emit very low frequencies (this is why we have always emphasized the bass or the reason why the super bass has no directivity). However, as the sound propagation distance increases, even typical directional speakers (such as horn speakers with 90° horizontal coverage angle and 90° vertical coverage angle) will obey the inverse square law, acting like a theoretical point source The diffusion of sound (ie, Omni directional radiation).
3. Line sound source
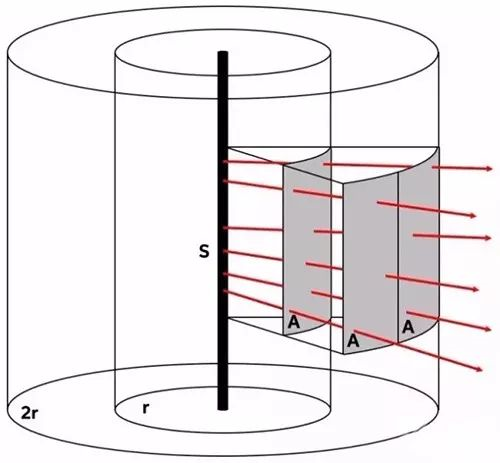
The sound pressure coverage of passive linear array speakers is close to the so-called line sound source theory. Whenever the listening distance is doubled, the level will not drop by 6dB. In theory, it will only drop by 3dB, but in practical applications, the result is not so ideal. As to why there are these differences, this article will not elaborate. But even so, compared to point source speakers, linear array speakers have unique advantages in terms of vertical coverage.
Speakers with linear sound source radiation characteristics can achieve the following effects: You can feel a relatively large sound pressure level in the back area of the hall or outdoor space, and in order to do this, you do not need to operate ordinary point sound source speakers. Similarly, the power is deliberately increased so that people who are closer to the PA system in front can hear too loud sounds. Its advantage lies in the complex and variable controllability of the vertical sound diffusion angle.
So how to achieve linear sound source radiation? The answer is phase cancellation.
Phase cancellation is usually one of the things that engineers try to avoid in audio systems, but it plays a central role in providing a narrow vertical coverage angle when line array speakers work together. Even if a high-level speaker cabinet design is used to shape the vertical coverage, there is still a lot of actual overlap between the speakers in the line array. In other words, the vertical coverage angle of a line array speaker cannot be formed by a single speaker, it is the result of effective interference of multiple speakers at the exit. However, in reality, the distance between each line array speaker and the audience will be slightly different, which will cause a small degree of phase cancellation. Of course, you can also manually intervene and make fine adjustments to the vertical coverage angle of line array speakers by introducing electronic delays (EAW Anya and Anna systems use this technology).
Precautions for the use of line array systems
Although the application of phase cancellation can form the effect of narrowing the vertical coverage angle of the speakers in the line array, their horizontal coverage angle is not affected. Therefore, a single speaker in a real line array can have a horizontal coverage angle of 90°, and only cover a vertical angle of 20° or less. In addition, even if phase cancellation can achieve line source distribution and significantly improve long-distance coverage, as the distance increases, the line array will begin to show point source characteristics, and succumb to the inverse square law that attenuates 6dB for every doubling of distance. .
The line array has the ability to approximate the line source function, but there are also some limitations and matters needing attention. First, the overall length of the array from top to bottom determines the lowest frequency with line sound source coverage characteristics. This is because as the wavelength becomes longer, at the listening position, the difference between the corresponding times when the sound reaches the listener's position from different speaker units must be larger to achieve the effect of a linear sound source. This requires a larger array length. At the other end of the spectrum, the wavelength becomes so short that the drivers are too large to be placed close enough together, so the relative phase difference becomes too large to realize the line source function. Under these circumstances, major manufacturers will use waveguide structures to realize the conversion from point sound sources to linear sound sources. Although all waveguide structures are for the same purpose, almost every manufacturer uses a different structure and has its own patent to protect its intellectual property rights. This is also the most difficult part of a manufacturer's process of developing linear array speakers.
Line arrays are very useful in acoustically challenging spaces because you can control their vertical spread and reduce sound reflections. Finding a way to get the sound coverage area away from the ceiling and floor is a good start, and then choose a speaker with a specific horizontal coverage angle, which will help you keep the excess sound away from the side walls, so as to get better indoor sound reinforcement clarity .

Line array form
Because the vertical radiation of each speaker is very narrow, the listening space can be effectively divided into multiple parts from front to back. The front is covered by only a small number of speakers, and more speakers can cover the rear. Based on this idea, a very popular J-shaped line array is formed, which often appears in concert halls and outdoor venues.
The exact installation shape of the line array will vary according to the layout and size of the area to be covered. In general, the front-row coverage only needs a small number of them to meet the sound pressure requirements because of the close distance, but the installation angle between the line arrays also needs to be designed to be larger because of the uniform coverage. However, because of the relatively long distance in the middle and rear, a larger number of speakers are required to be installed at a concentrated angle, so that the effect of long-distance coverage can be achieved. The approach outlined just now helps to improve the consistency of overall coverage. In recent years, there has also been developed a way for users to fine-tune the distribution of energy by adjusting the power delivered to each speaker box-this technique is usually called power gradation.
Challenges and limitations of line arrays
Although line arrays can help solve certain spatial problems, they have complex limitations. In addition to the challenge of requiring sufficient length to control the coverage angle of lower frequencies, line arrays may sometimes suffer from strange anomalies, for example, certain frequencies may form lobes in the area directly above and below the array. If this happens to happen in a bad acoustic space, it may bring serious consequences. For example, if your vocal microphone is placed under the line array, you may experience feedback problems.
Line array settings
For the line array to play its role well, it needs to go through a strict mechanical installation design, and set up the correct electronic frequency division and calibration procedures. Because of the complex interactions involved, all of this is important. The exact installation angle of each cabinet, the exact hanging point and height, as well as the individual driver and delay, phase, gain and even high and low pass filter settings of each cabinet must be precise to achieve the best performance . Fortunately, most of the existing big-brand manufacturers have software for sound coverage simulation based on virtual space for their products.
Sound quality
Even in the best case, a line array cannot match the purity of the sound produced by a high-quality single-drive speaker or a single two-way or three-way drive speaker. This is one reason why they are unlikely to appear in a small space. For small occasions, it would be more suitable if the number of speakers that can produce sound can be less. Of course, cost and space are also considerations.
Micro line array
Although line array technology is most commonly used in professional large-scale indoor and outdoor sound reinforcement applications, there are many companies, such as Bose, Turbosound, etc., that provide small personal PA systems that use small speaker arrays (usually 2"-4" Size) to produce the same line source coverage effect. The correct use of these systems can allow them to provide good coverage in small venues.

 English
English










